Explore the offer
Upscale to Intermediate TRL / Nano/Micro Layer Analysis
X-Ray Reflectivity
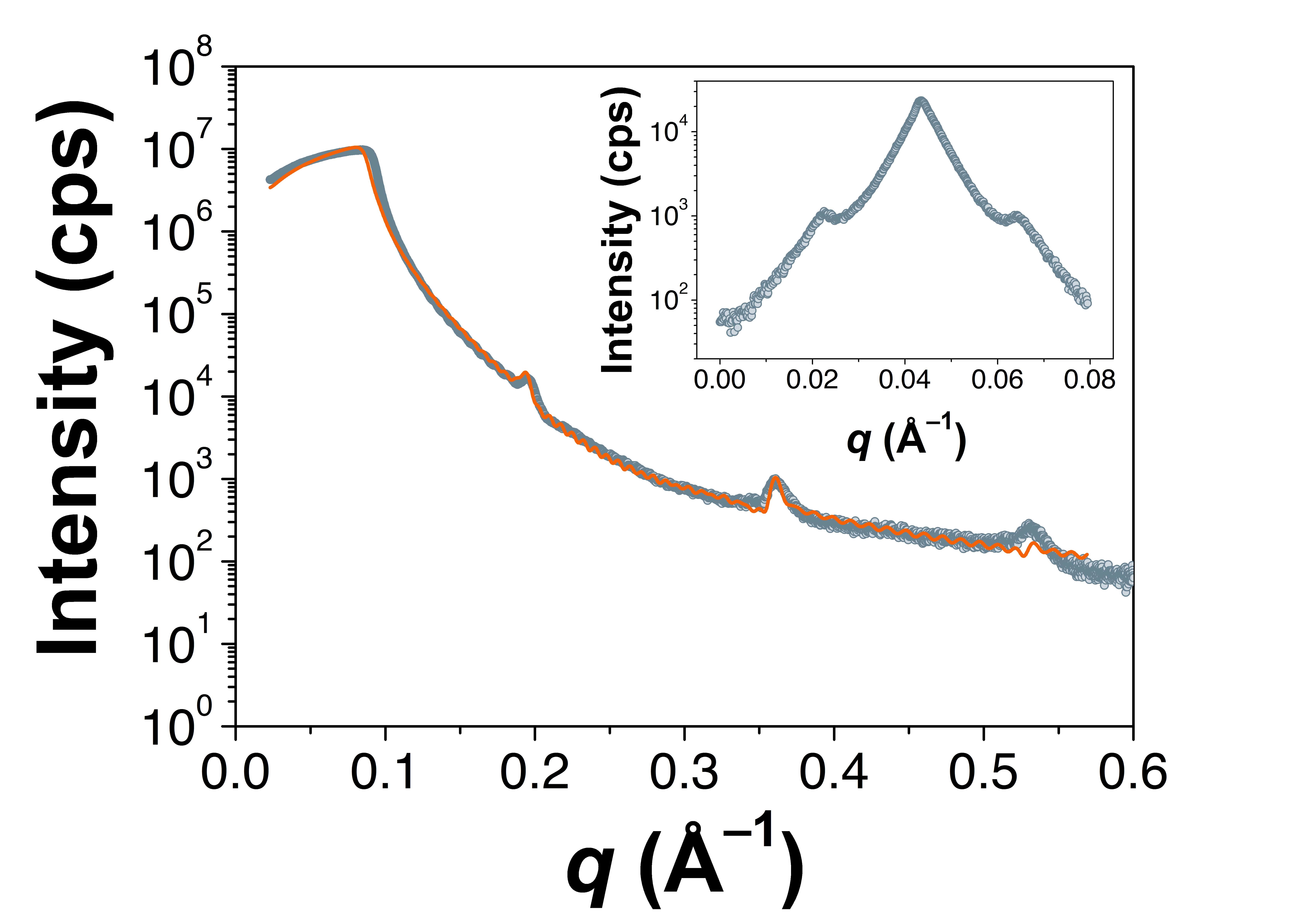
X-ray Reflectivity (XRR) is a grazing incidence X-ray elastic scattering technique sensitive to surface electron densities. In the X-ray range, the index of refraction is slightly less than one and indeed, as a surface is illuminated with a collimated X-ray beam, total external reflection occurs up to the critical angle, which depends on the wavelength of the X-ray beam and the electron density of the material.
Above the critical angle, the intensity of the reflected X-ray beam decreases exponentially with increasing the incidence angle. The intensity of the beam entering the material likewise increases with the incidence angle and decreases with depth according to the Beer-Lambert law. If the beam crosses interfaces between materials having different electron densities, interference effects are detected that modulate the overall reflected intensity and produce oscillations known as Kiessig fringes. The thickness of the various layers impact on the periodicity of these fringes while surface/interface roughness reduces the overall reflected intensity.

Available instruments
Select instruments to view their specifications and compare them (3 max)
Lab's Facility
Catania
CNR-IMM@CT
Lecce