Explore the offer
Advanced Characterization and Fine Analysis / Electron spectroscopy
Photo-Electron Spectroscopy
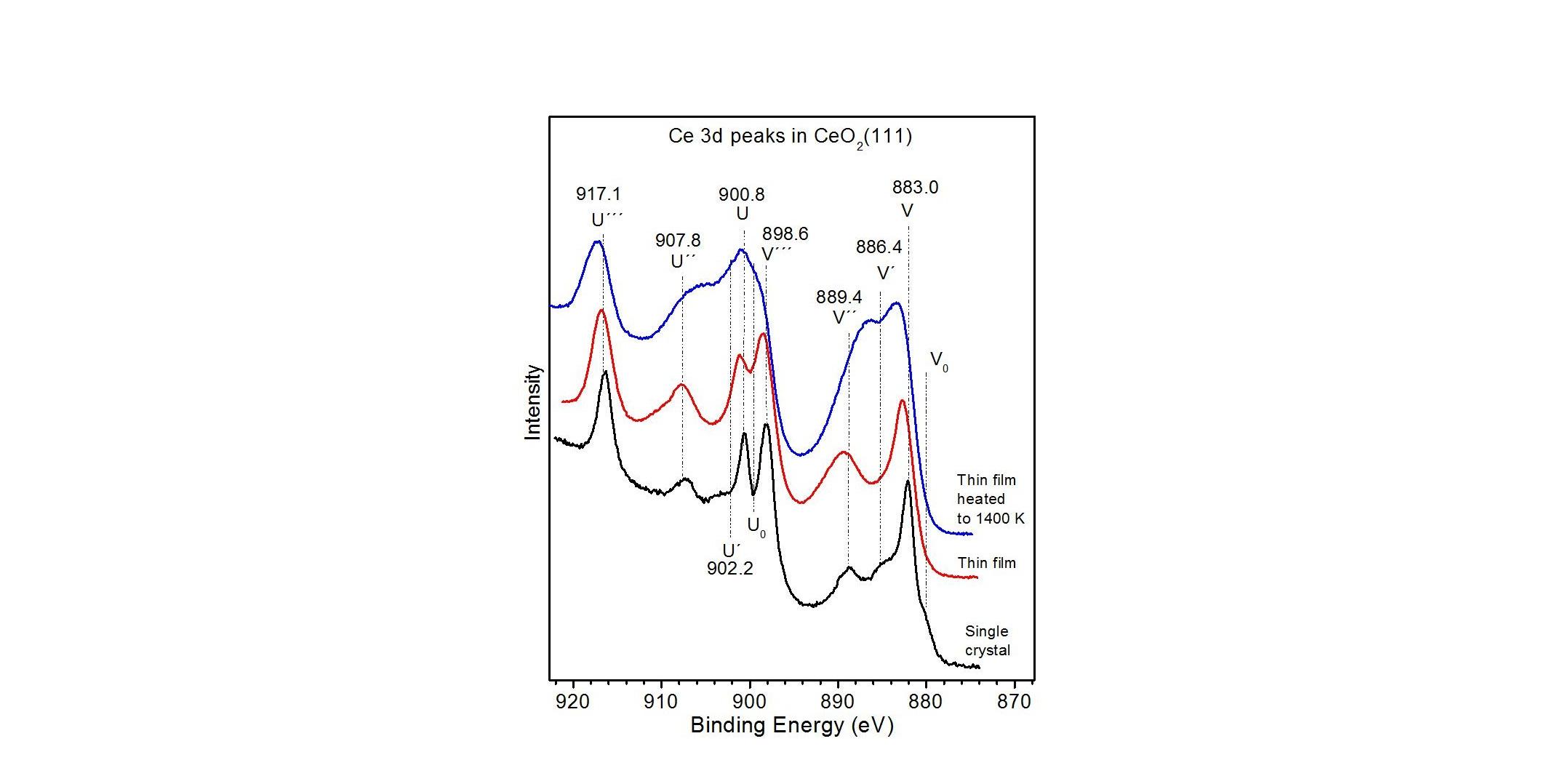
PES (Photo-electron Spectroscopy) is a general term that includes X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), also known as Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA), and Ultraviolet Photoelectron Spectroscopy (UPS), that are the most used techniques for the investigation of the chemical properties of the material. In PES, a monochromatic photon beam impinges on the sample and extracts photoelectrons. These photoelectrons are then collected by an electrostatic lens system; their energy dispersion is then measured by an electron energy analyzer. The collected data form the so-called electron dispersion curve (EDC) or photoemission spectrum. From the analysis of the photoemission spectrum, it is possible to derive the chemical composition (stoichiometry) of the material under study and several information about the chemical state of each element, such as oxidation state, chemical bonds, etc. PES can be exploited as a surface chemical analysis technique: the valence band DOS (assessable by UPS) reveals the orbital contributions through cross-section analysis (photon energy dependence) and core level photoemission (assessable by XPS) is sensitive to the local environment of a given atomic species in the first atomic layers of the sample.

Available instruments
Select instruments to view their specifications and compare them (3 max)
Lab's Facility
Trieste
CNR-IOM@TS
Trieste
CNR-IOM@TS
Napoli