Explore the offer
Advanced Characterization and Fine Analysis / Electron, Ion and photon beam microscopy
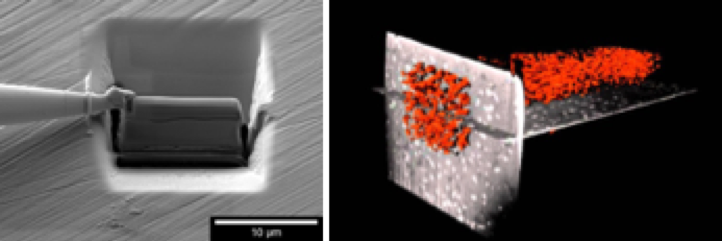
FIB-SEM for 3D reconstruction and TEM lamellae preparation
Plasma FIB-SEM (Focused Ion Beam-Scanning Electron Microscope) systems represent cutting-edge technology for high-resolution imaging, precise material characterization, and nanoscale fabrication. By integrating the functionalities of a focused ion beam with a scanning electron microscope, these systems capitalize on the advantages of plasma ion sources to deliver superior performance.
The most traditional ion source is gallium (Ga+), which offers a great versatility of use and a high degree of surface polishing, with minimization of the amorphous thickness.
At AREA laboratory, the gallium source is complemented with a plasma ion source in xenon (Xe), capable of offering significantly higher milling rates compared to the traditional one. This capability facilitates rapid material removal and large-volume 3D analyses. It also include a variety of detectors for secondary electrons (SE) and backscattered electrons (BSE), enabling comprehensive material characterization. The FIB is capable of creating high-resolution 3D reconstructions through sequential milling and imaging. Furthermore, the integration with additional analytical techniques such as Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) enhances their analytical capabilities.
The FIB-SEM is ideal for the semiconductor and material science industries, providing critical insights into structures at the nanoscale. It is also excellent for preparing samples for Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and other high-resolution analytical techniques, utilizing a Nanomanipulator for lamellae extraction, allowing the control of the lamellae thickness.
These advanced tools are designed to meet the stringent demands of modern research and industrial environments.

Available instruments
Select instruments to view their specifications and compare them (3 max)
Lab's Facility
Trieste
AREA-RIT
Bologna