Explore the offer
Advanced Characterization and Fine Analysis / Scanning probe microscopy
Scanning Field Emission Microscopy
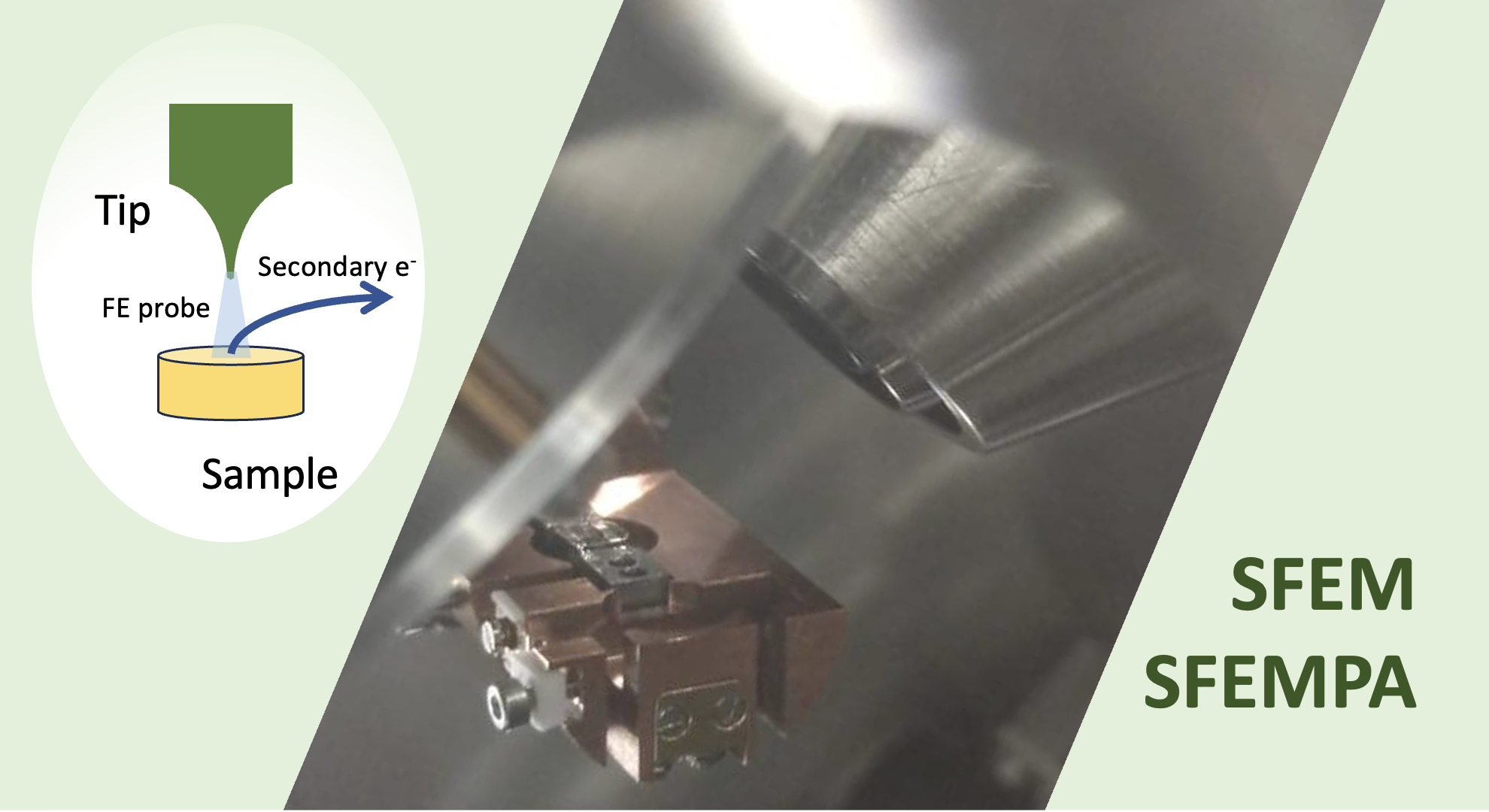
By scanning a tip in the proximity of a surface, like in a STM, the local properties of the surface can be observed via the secondary electrons emitted at probing the sample with the field-emitted electrons from the tip. Polarization analysis of secondary electrons can be also applied.
The methodology of scanning the tip at tip-to-surface distance in the domain for field-emission is called SFEM (Scanning Field Emission Microscopy) or NFESEM (Near Field Emission SEM). SFEMPA in case the electron spin of emitted electrons is also analyzed. The Near-Field character of the probe makes this methodology significantly different from remote-source SEM (where Field-Emission is commonly used today for the monochromaticity of a cold electron source), and still distinguishes the process from what occurs in STM where tip and sample orbitals are directly coupled by tunneling trough a vacuum barrier. Among the relevant possibilities, an interesting one is introduced by using magnetized tips for the imprinting of a polarized nature to the electron probe.
