Explore the offer
Upscale to Intermediate TRL / Electrical Analysis
RF VNA characterization with probe station
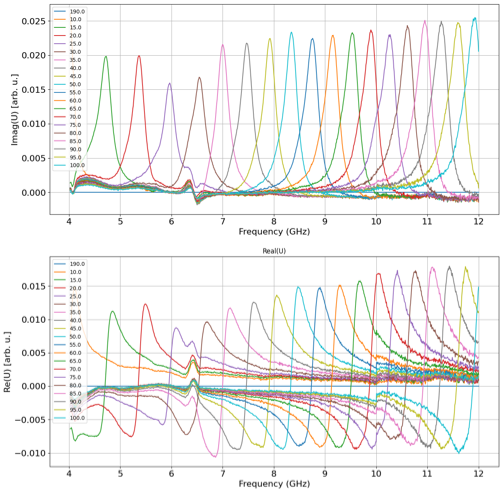
The Vector Network Analyser is typically used to characterize the electrical response of a system as a function of frequency (from 10 MHz up to 40 GHz). The tool can apply a calibrated electrical stimulus of specific frequency and measure the reflected/transmitted voltage and current both in magnitude and phase. The resulting measurement presents a detailed electrical characterization of the system in terms of equivalent impedance of the network or device under test (DUT) as a function of frequency throughout the measured frequency range. Obtaining this information as a function of frequency enables detailed electrical description of complex electrical response in a simple and concise way. The technique is extremely powerful in the sense that it can provide complete electrical response information on any linear electrical system. It is commonly used to measure high frequency devices as well as measure the material properties in extended frequency ranges. The VNA can be coupled with an external dipole/quadrupole electromagnet to perform broadband FMR and spin wave spectroscopy. FMR VNA is a powerful all electric experimental technique that can be used to resolve fundamental material properties (e.g. saturation magnetization, damping coefficient, gyromagnetic ratio). The FMR VNA can sweep the frequency of the input signal and measure reflected/transmitted signal while the external magnet can sweep the magnetic field providing much bigger set of data. The quadrupole magnet can generate a vectorial magnetic field tunable in the sample plane with a maximum intensity > 0.2 T (> 0.15 T in the dipolar configuration). The sample is excited by passing the RF signals through a standing coplanar waveguide (CPW) over which the sample is positioned. The VNA setup can be used to detect spin waves propagating in the magnetic ordering of a material under study. The VNA can be connected to a pair of parallel microwave antennas through RF microprobes (e.g. coplanar waveguides and ground-signal-ground (GSG) RF probes). Each microstrip is connected to a separate port of the VNA. Spin waves are excited from the first antenna (transmitter) and detected by the second one (receiver). This analysis is most useful to understand the behavior of magnetic materials.

Available instruments
Select instruments to view their specifications and compare them (3 max)
Lab's Facility
Milano